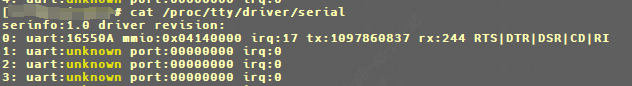
1 引入UART工作原理#
uart硬件传输原理。s3c2440裸机编程-UART体系。
2 Linux下TTY驱动框架#
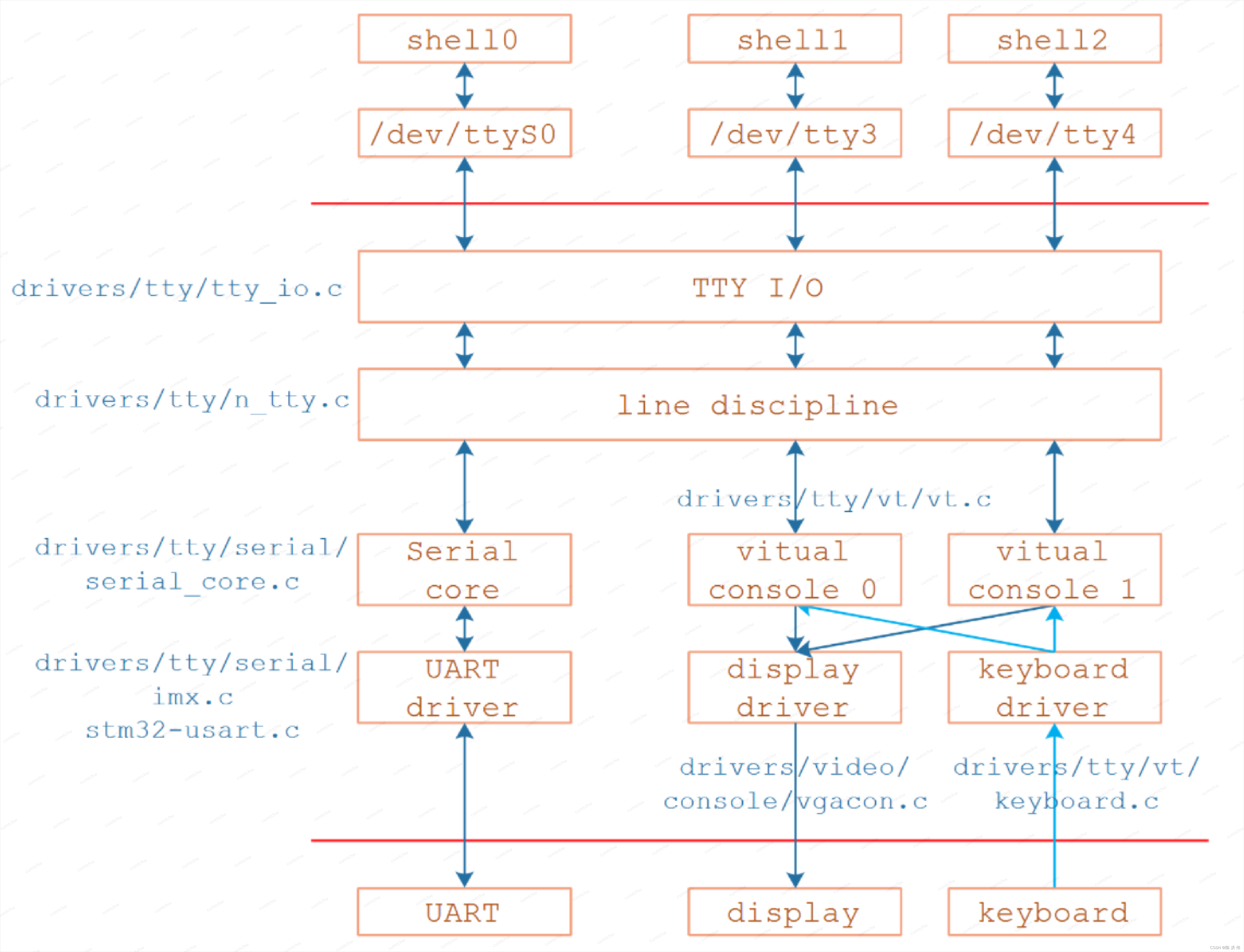
可以看到tty框架下不止包含uart,还有display设备,键盘设备。
详细展开如下,tty_driver位于tty_io.c, 调用底下的uart_diver位于serial_core.c。uart_driver子系统会被最底层的soc厂商拿去适配,调用uart_register_driver注册自己的uart控制器,去实现控制器要实现的uart_fops操作函数。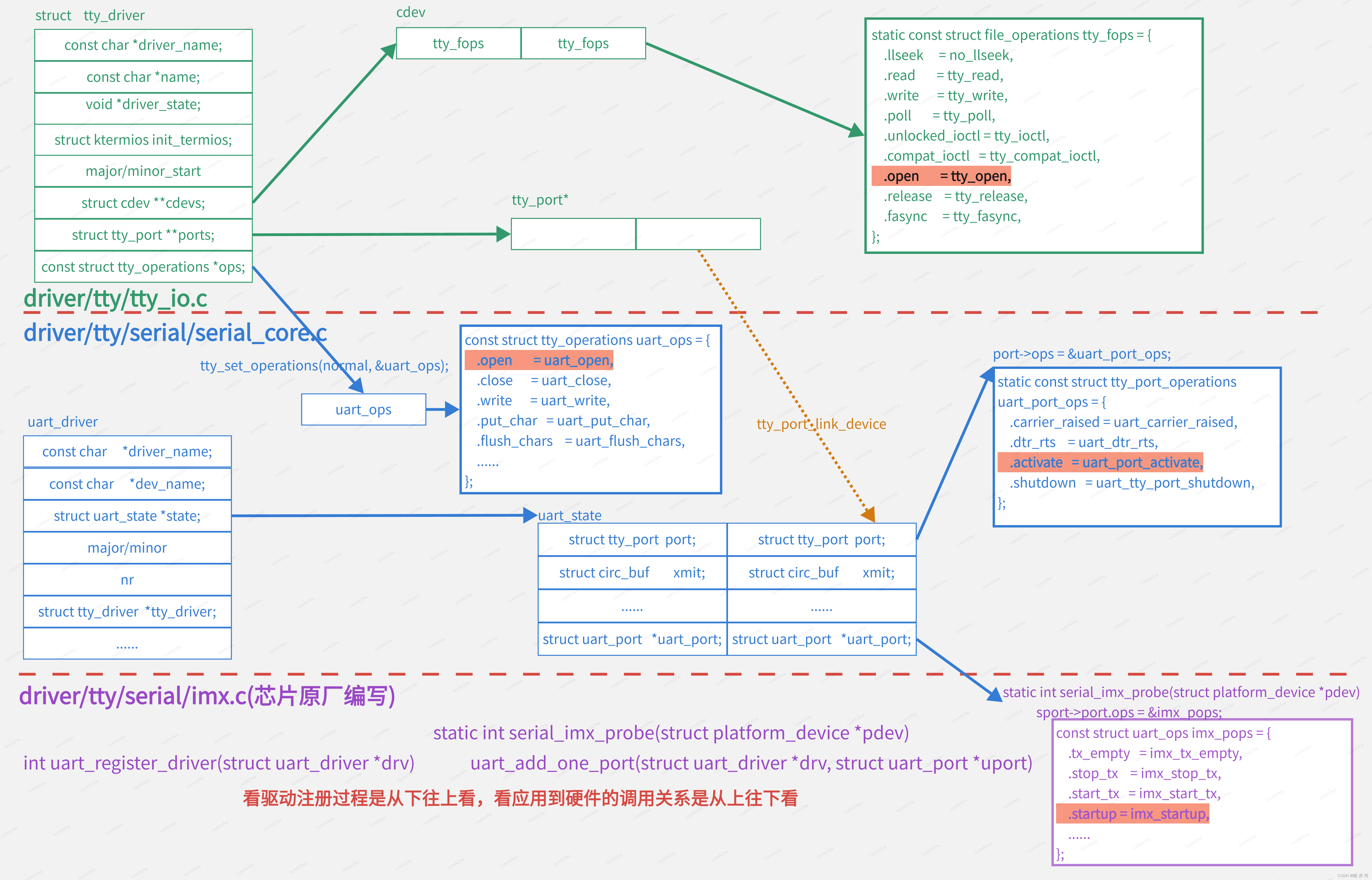
2.1 设备节点差别#
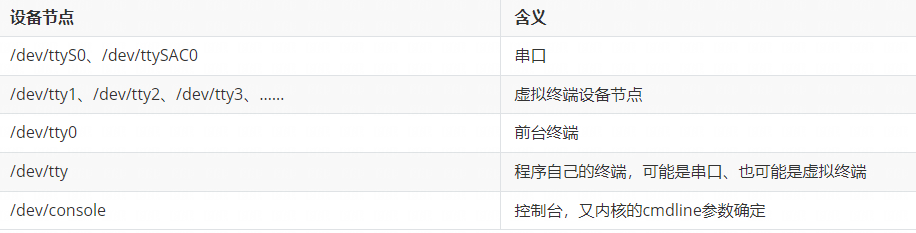
2.1.1 串口终端(/dev/ttyS*)#
串口终端是使用计算机串口连接的终端设备。Linux把每个串行端口都看做是一个字符设备。这些串行端口所对应的设备名称是/dev/ttySAC*;
2.1.2 控制台终端(/dev/console)#
在Linux系统中,计算机的输出设备通常被称为控制台终端,这里特指printk信息输出到设备。/dev/console是一个虚拟的设备,它需要映射到真正的tty上,比如通过内核启动参数“console=ttySCA0”就把console映射到了串口0
2.1.3 虚拟终端(/dev/tty*)#
当用户登录时,使用的是虚拟终端。使用Ctcl+Alt[F1 - F6]组合键时,我们就可以切换到tty1、tty2、tty3等上面去。tty*就称为虚拟终端,而tty0则是当前所使用虚拟终端的一个别名。
2.2 架构层次#
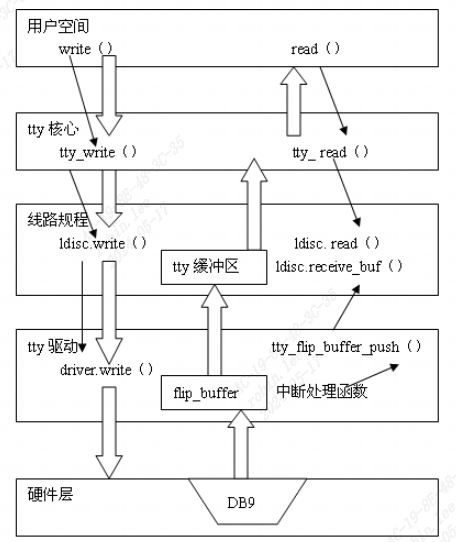
TTY核心层->线路规划层->tty驱动层。
2.3 UART驱动子系统#
2.3.1 数据结构和API#
2.3.1.1 uart_driver#
1 | struct uart_driver { |
2.3.1.1.1 uart_driver 注册与注销#
int uart_register_driver(struct uart_driver *drv);
返回值:0,成功;负值,失败。
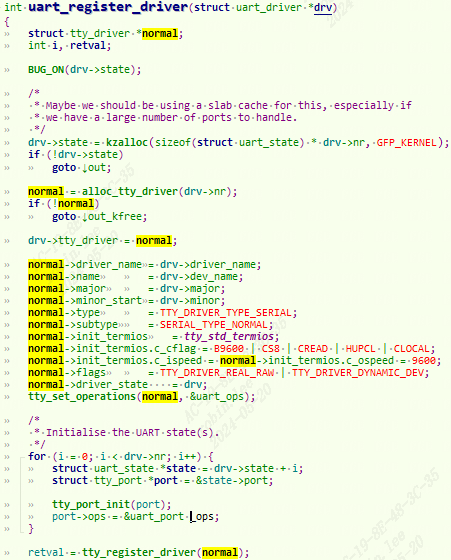
1 | retval = tty_register_driver(normal); |

设置uart_ops为tty的tty_operations。然后调用tty_register_driver注册到tty子系统。
void uart_unregister_driver(struct uart_driver *drv);
2.3.1.2 uart_port#
描述串口端口的I/O端口或I/O内存地址、FIFO大小、端口类型、串口时钟等信息。实际上,一个uart_port实现对应一个串口设备。
1 | struct uart_port { |
2.3.1.2.1 uart_port 的添加与移除#
int uart_add_one_port(struct uart_driver *drv, struct uart_port *uport);
返回值:0,成功;负值,失败。
uart_port 和 uart_driver 结合起来。
int uart_remove_one_port(struct uart_driver *drv, struct uart_port *uport);
2.3.1.2.2 uart_port 的休眠与恢复#
1 | int uart_suspend_port(struct uart_driver *drv, struct uart_port *port);//挂起特定的串口端口 |
2.3.1.3 uart_ops#
1 | struct uart_ops { |
2.3.1.4 console#
1 | struct console { |
2.3.1.5 波特率相关#
1 | /*功能:uart_get_baud_rate通过解码termios结构体来获取指定串口的波特率 |
2.3.1.6 向串口写控制台信息#
1 | /*功能:uart_console_write用于向串口端口写一控制台信息 |
2.4 UART控制器示例-imx为例#
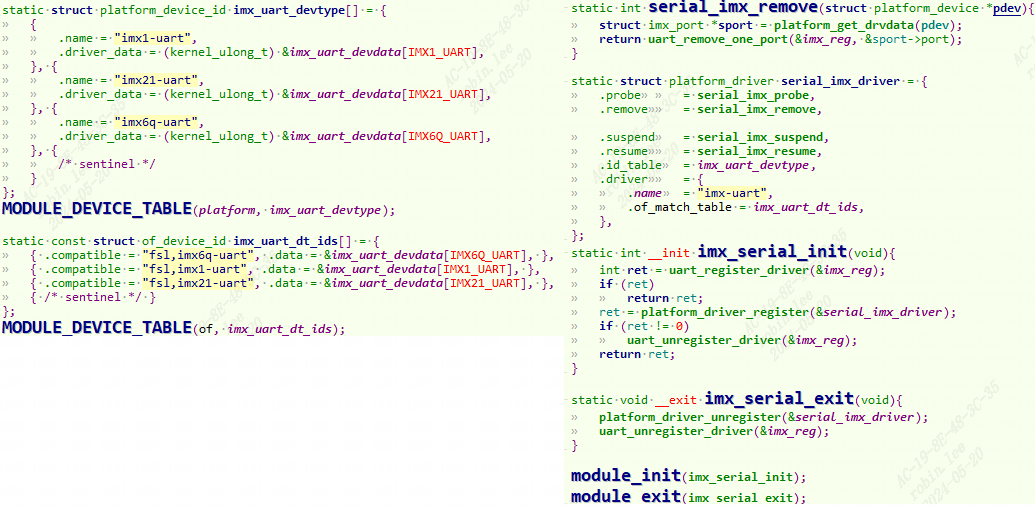
位于drivers\tty\serial\imx.c,使用platform_driver框架,调用uart_register_driver注册到uart子系统。
2.4.1 dts描述#
板子使用的是uart3,打开imx6ul.dtsi,可以看到默认status是disabled。
1 | uart3: serial@021ec000 { |
我们再外面引用它,打开imx6ull-alientek-emmc.dts:
1 | pinctrl_uart3: uart3grp { |
2.4.2 probe初始化#
当dts和驱动的compatible匹配,那么probe执行如下:
初始化 uart_port,然后将其添加到对应的 uart_driver 中。
- 解析dts, 设置中断号,io基地址后
ioremap, 设置port属性。

- 设置port属性的ops
- 更具dts获取和设置时钟频率。
- 注册中断
uart_add_one_port(&imx_reg, &sport->port);添加端口到uart_driver。
2.4.2 收据收发流程#
2.4.2.1 open过程#
1 | //tty_io.c |
1 | static int uart_open(struct tty_struct *tty, struct file *filp) { |
2.4.2.2 发送接收总流程#
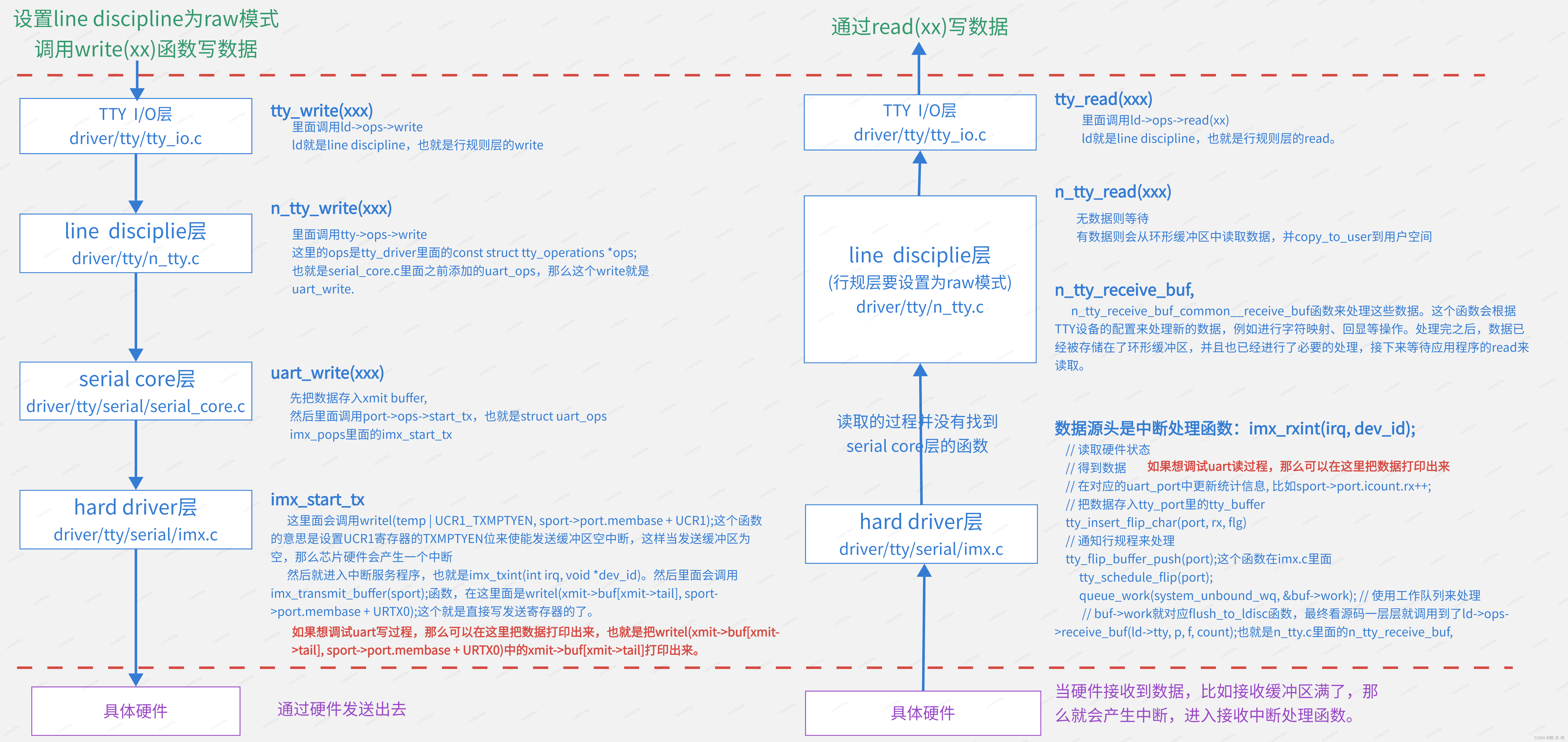
2.4.2.3 发送-write过程#
1 | 1. 应用层调用write系统调用来写入数据 |
2.4.2.3.1 用户写数据流程#
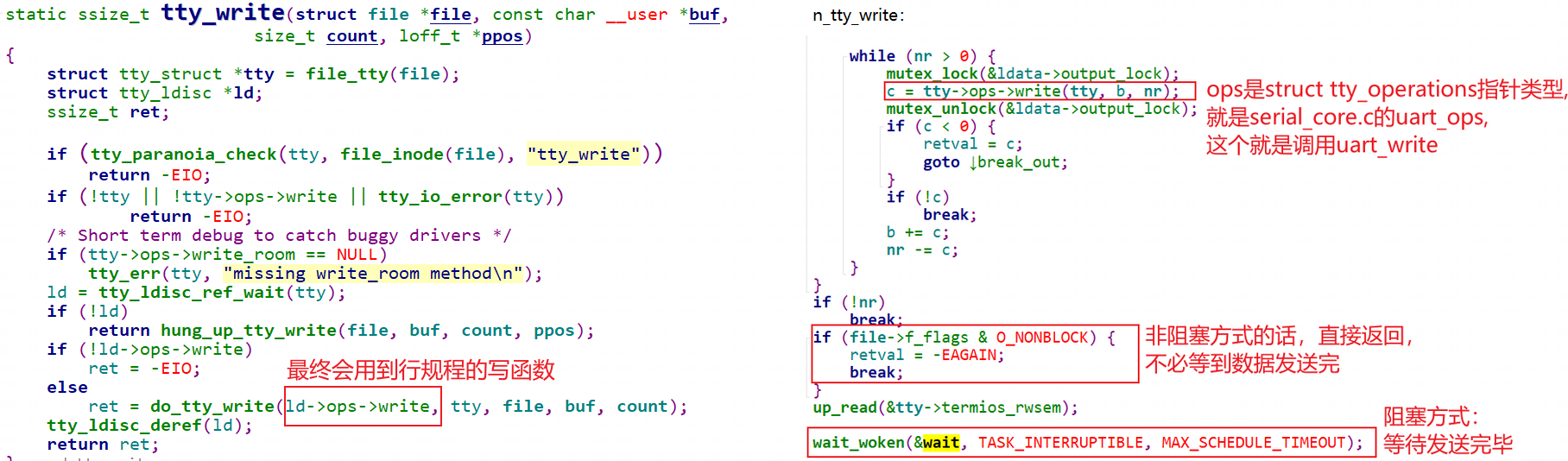

在tty_write中通过ld->ops->write调用了线路规程的write函数,也就是调用了tty_ldisc_N_TTY的ntty_write函数。
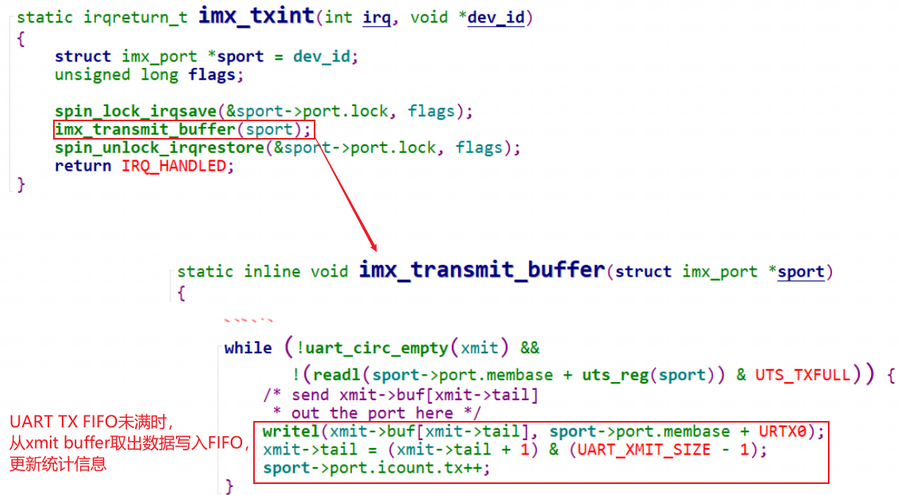
2.4.2.3.2 硬件写数据流程#
drivers\tty\serial\imx.c的发送函数imx_start_tx和发送中断函数imx_txint。

一开始时,发送buffer肯定为空,会立刻产生中断:
2.4.2.4 接收-read过程#
1 | 1. UART硬件控制器的接收端接收到数据后,数据会被自动写入接收缓冲区。 |
2.4.2.4.1 中断产生数据流程#
imx_rxint
// 读取硬件状态
// 得到数据
// 在对应的uart_port中更新统计信息, 比如sport->port.icount.rx++;
// 把数据存入tty_port里的tty_buffer
tty_insert_flip_char(port, rx, flg)
// 通知行规程来处理
tty_flip_buffer_push(port);
tty_schedule_flip(port);
queue_work(system_unbound_wq, &buf->work); // 使用工作队列来处理
// 对应flush_to_ldisc函数
2.4.2.4.2 用户读取数据流程#
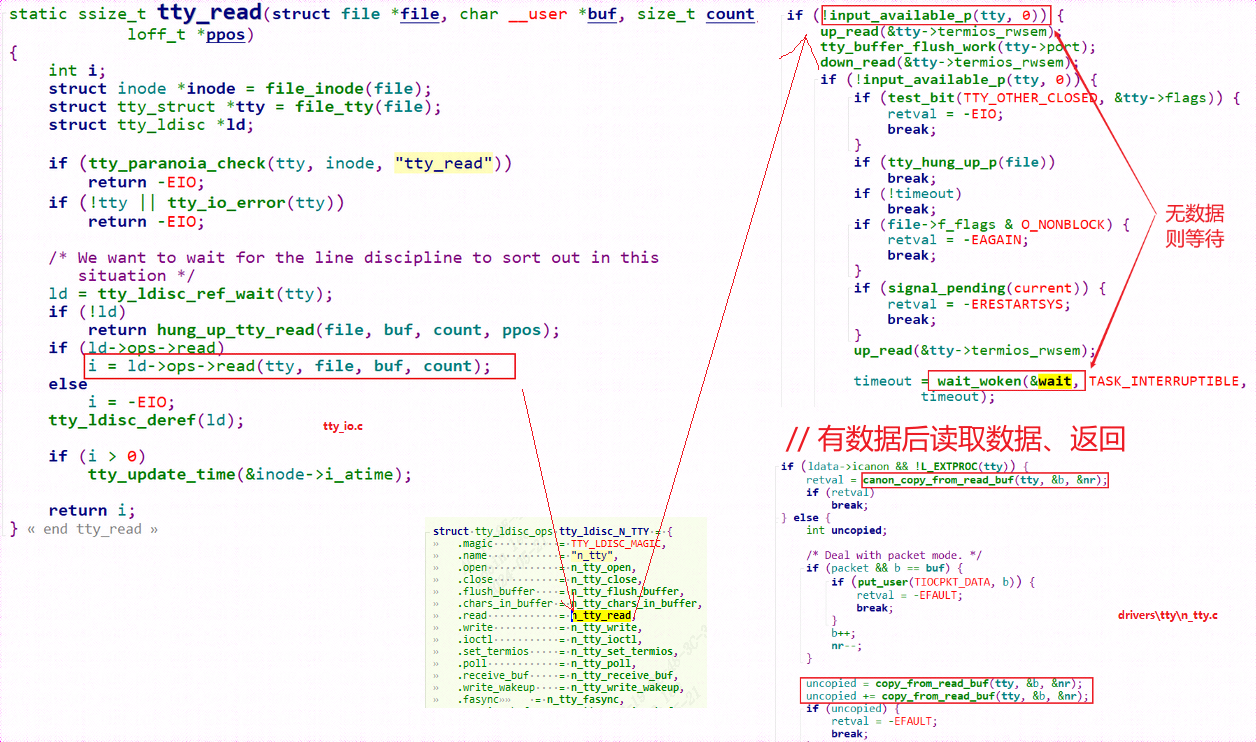
在tty_read中通过ld->ops->read调用了线路规程的read函数,也就是调用了tty_ldisc_N_TTY的ntty_read函数。
3 UART用户态控制函数#
3.1 API说明#
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| tcgetatrr | 取属性(termios结构) |
| tcsetarr | 设置属性(termios结构) |
| cfgetispeed | 得到输入速度 |
| cfsetispeed | 得到输出速度 |
| cfstospeed | 设置输出速度 |
| tcdrain | 等待所有输出都被传输 |
| tcflow | 挂起传输或接收 |
| tcflush | 刷请未决输出和/或输入 |
| tcsendbreak | 送BREAK字符 |
| tcgetpgrp | 得到前台进程组ID |
| Tcsetpgrp | 设置前台进程组ID |
3.1.1 设置参数#
- 获取属性,
tegetatrr(fd, &oldtio);
1 | struct termious newtio, oldtio; |
- 激活选项有
CLOCAL和CREAD,用于本地连接和接收使用
1 | newtio.cflag |= CLOCAL|CREAD; |
- 设置波特率
1 | newtio.c_cflag = B115200; |
- 设置数据位,需使用掩码设置
1 | newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; |
- 设置停止位,通过激活
c_cflag中的CSTOP实现。若停止位为1,则清除CSTOPB,若停止位为2,则激活CSTOP
1 | newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; /*停止位设置为1*/ |
- 设置流控
1 | newtio.c_cfag |= CRTSCTS /*开启硬件流控 */ |
- 奇偶检验位设置,使用
c_cflag和c_ifag.
7.1 设置奇校验
1 | newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB; |
7.2 设置偶校验
1 | newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP); |
- 设置最少字符和等待时间,对于接收字符和等待时间没有什么特别的要求,可设置为0:
1 | newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0; |
- 处理要写入的引用对象
tcflush函数刷清(抛弃)输入缓冲(终端程序已经接收到,但用户程序尚未读)或输出缓冲(用户程序已经写,但未发送)。
1 | int tcflash(int filedes, int quene) |
- 激活配置,在完成配置后,需要激活配置使其生效。使用
tcsetattr()函数:
1 | int tcsetarr(int filedes, const struct termios *termptr); |
3.1.2 操作流程#
- 打开串口,例如
"/dev/ttySLB0"
1 | fd = open("/dev/ttySLB0",O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY); |
- 恢复串口状态为阻塞状态,用于等待串口数据的读入,用fcntl函数:
1 | fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,0); //F_SETFL:设置文件flag为0,即默认,即阻塞状态 |
- 接着测试打开的文件描述符是否应用一个终端设备,以进一步确认串口是否正确打开。
1 | isatty(STDIN_FILENO); |
- 读写串口
1 | 串口的读写与普通文件一样,使用read,write函数 |
3.2 demo举例#
1 |
|