1 gpio 子系统引入 如果 pinctrl 子系统将一个 PIN 复用为 GPIO 的话,那么接下来要用到 gpio 子系统了。gpio 子系统顾名思义,就是用于初始化 GPIO 并且提供相应的 API 函数,比如设置 GPIO为输入输出,设置读取 GPIO 的值等。
gpio 子系统的主要目的就是方便驱动开发者使用 gpio,驱动开发者在设备树中添加 gpio 相关信息,然后就可以在驱动程序中使用 gpio 子系统提供的 API函数来操作 GPIO,Linux 内核向驱动开发者屏蔽掉了 GPIO 的设置过程,极大的方便了驱动开发者使用 GPIO。
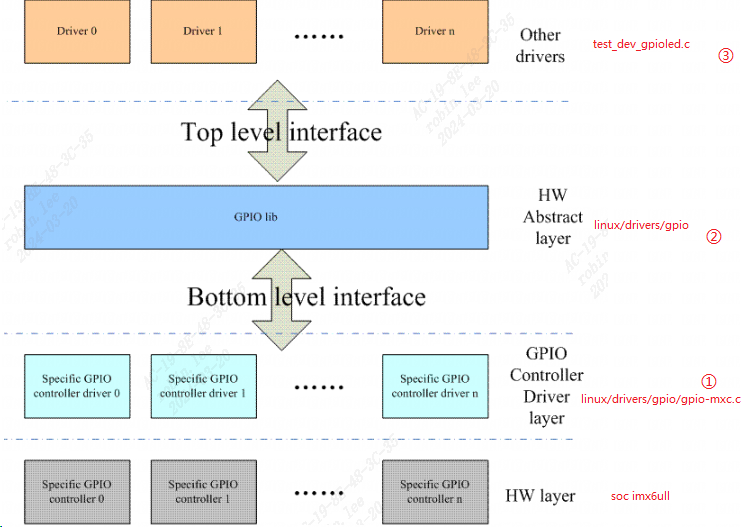
2 gpio子系统架构 Linux的GPIO子系统驱动框架由三个主要部分组成:① GPIO控制器驱动程序、②gpio lib驱动程序 ③GPIO字符设备驱动程序:gpiochip_add/gpiochip_add_data向系统注册gpio_chip, 这些都是半导体原厂要做的,设备商只需要使用即可。
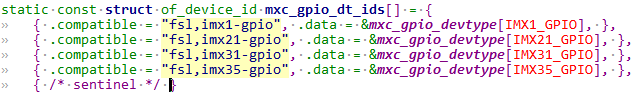
2.0 gpio控制器源码分析 drivers/gpio/gpio-mxc.c 就是 I.MX6ULL的 GPIO 控制器驱动文件,在此文件中有如下所示of_device_id 匹配表:imx6ull.dtsi的gpio控制器可以看到能匹配:
打开drivers/gpio/gpio-mxc.c:
点击查看代码
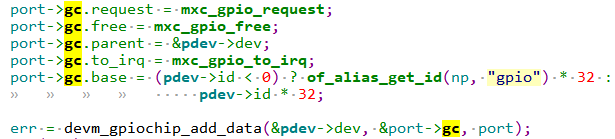
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 static int mxc_gpio_probe (struct platform_device *pdev) { struct device_node *np = struct mxc_gpio_port *port ; struct resource *iores ; int irq_base = 0 ; int err; mxc_gpio_get_hw(pdev); port = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof (*port), GFP_KERNEL); if (!port) return -ENOMEM; iores = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0 ); port->base = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, iores); if (IS_ERR(port->base)) return PTR_ERR(port->base); port->irq_high = platform_get_irq(pdev, 1 ); port->irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0 ); if (port->irq < 0 ) return port->irq; port->clk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, NULL ); if (IS_ERR(port->clk)) port->clk = NULL ; err = clk_prepare_enable(port->clk); if (err) { dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Unable to enable clock.\n" ); return err; } pm_runtime_set_active(&pdev->dev); pm_runtime_enable(&pdev->dev); err = pm_runtime_get_sync(&pdev->dev); if (err < 0 ) goto out_pm_dis; writel(0 , port->base + GPIO_IMR); writel(~0 , port->base + GPIO_ISR); if (mxc_gpio_hwtype == IMX21_GPIO) { irq_set_chained_handler(port->irq, mx2_gpio_irq_handler); } else { irq_set_chained_handler_and_data(port->irq, mx3_gpio_irq_handler, port); if (port->irq_high > 0 ) irq_set_chained_handler_and_data(port->irq_high, mx3_gpio_irq_handler, port); } err = bgpio_init(&port->gc, &pdev->dev, 4 , port->base + GPIO_PSR, port->base + GPIO_DR, NULL , port->base + GPIO_GDIR, NULL , BGPIOF_READ_OUTPUT_REG_SET); if (err) goto out_bgio; if (of_property_read_bool(np, "gpio_ranges" )) port->gpio_ranges = true ; else port->gpio_ranges = false ; port->gc.request = mxc_gpio_request; port->gc.free = mxc_gpio_free; port->gc.parent = &pdev->dev; port->gc.to_irq = mxc_gpio_to_irq; port->gc.base = (pdev->id < 0 ) ? of_alias_get_id(np, "gpio" ) * 32 : pdev->id * 32 ; err = devm_gpiochip_add_data(&pdev->dev, &port->gc, port); if (err) goto out_bgio; irq_base = irq_alloc_descs(-1 , 0 , 32 , numa_node_id()); if (irq_base < 0 ) { err = irq_base; goto out_bgio; } port->domain = irq_domain_add_legacy(np, 32 , irq_base, 0 , &irq_domain_simple_ops, NULL ); if (!port->domain) { err = -ENODEV; goto out_irqdesc_free; } err = mxc_gpio_init_gc(port, irq_base, &pdev->dev); if (err < 0 ) goto out_irqdomain_remove; list_add_tail(&port->node, &mxc_gpio_ports); platform_set_drvdata(pdev, port); pm_runtime_put(&pdev->dev); return 0 ; out_pm_dis: pm_runtime_disable(&pdev->dev); clk_disable_unprepare(port->clk); out_irqdomain_remove: irq_domain_remove(port->domain); out_irqdesc_free: irq_free_descs(irq_base, 32 ); out_bgio: dev_info(&pdev->dev, "%s failed with errno %d\n" , __func__, err); return err; }
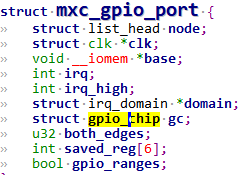
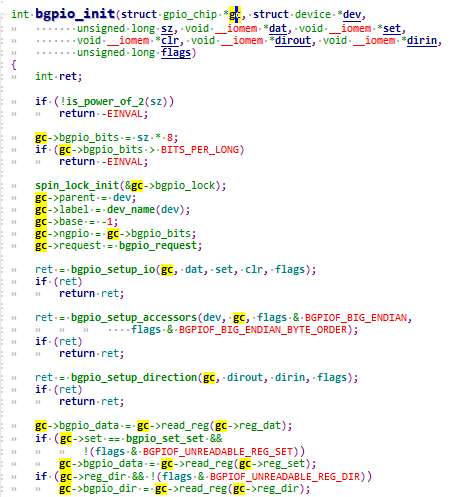
2.0.1 probe分析 里面定义了一个很重要的结构体mxc_gpio_port 就是对 I.MX6ULL GPIO 的抽象。mxc_gpio_port 结构体定义如下:mxc_gpio_probe又会继续调用mxc_gpio_get_hw获取gpio的硬件相关数据,也就是gpio组,gpio1.gpio2等。
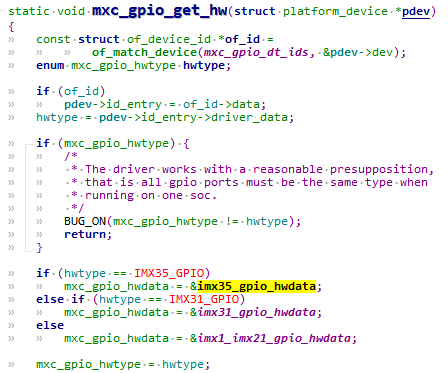
2.0.1.0 mxc_gpio_get_hw
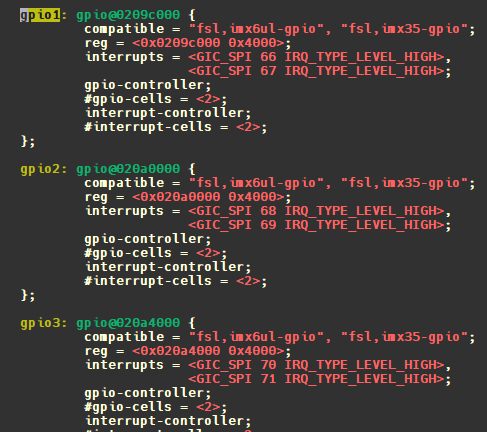
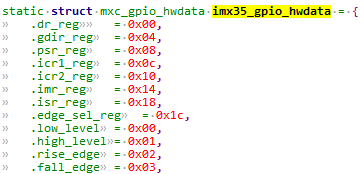
我们imx6ull gpio控制器类型就是imx35系列。因此选用imx35_gpio_hwdata,如下:可以看出这些成员不就是对应寄存器的偏移量吗?
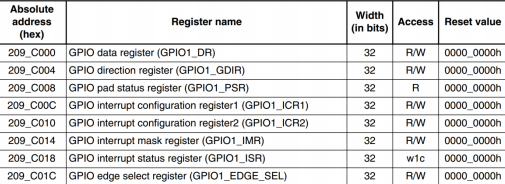
2.0.1.1 get resource and ioremap 比如我们probe中通过platform_get_resource 获取gpio1的基地址为0X0209,C000,那么就可以通过配置mxc_gpio_hwdata结构体成员来配置寄存器。
然后调用 devm_ioremap_resource 函数进行内存映射,得到 0x0209C000 在 Linux 内核中的虚拟地址。platform_get_irq 函数获取中断号,分为获取高 16 位 GPIO 的中断号,和获取低 16 位 GPIO 中断号。
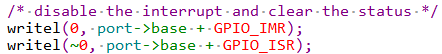
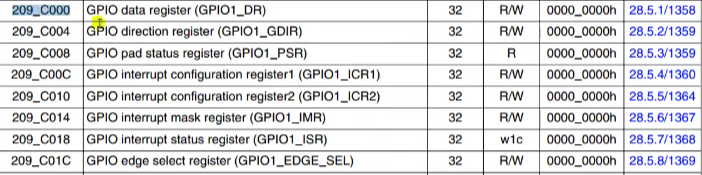
操作 GPIO1 的 IMR 和 ISR 这两个寄存器,关闭 GPIO1 所有 IO 中断,并且清除状态寄存器:
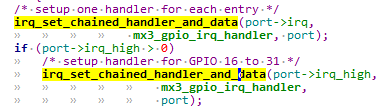
设置对应 GPIO 的中断服务函数,不管是高 16 位还是低 16 位,中断服务函数都是 mx3_gpio_irq_handler:
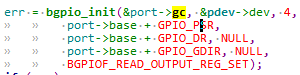
2.0.1.2 bgpio_init
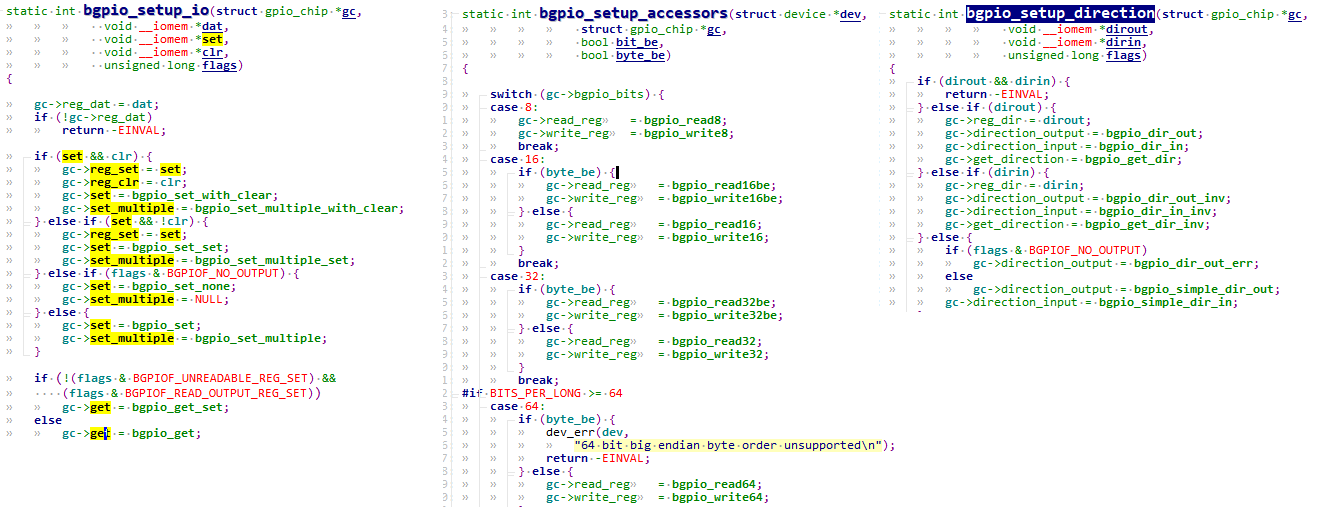
调用bgpio_init 函数主 要 任 务 就 是 初 始 化 port->gc, (gc就是gpio_chip)。顾名思义bgpio_init就是basic gpio init,里 面 有 三 个 setup 函 数 :
bgpio_setup_io bgpio_setup_accessors bgpio_setup_direction。这三个函数就是初始化 port->gc 中的各种有关GPIO 的操作,比如输出,输入等等。
2.0.1.3 devm_gpiochip_add_data 调用devm_gpiochip_add_data注册这个port。gpio控制器就成功注册给了gpio子系统。
至此,port->gc既有了对 GPIO 的操作函数,又有了 I.MX6ULL 有关 GPIO的寄存器,那么只要得到 port 就可以对 I.MX6ULL 的 GPIO 进行操作。
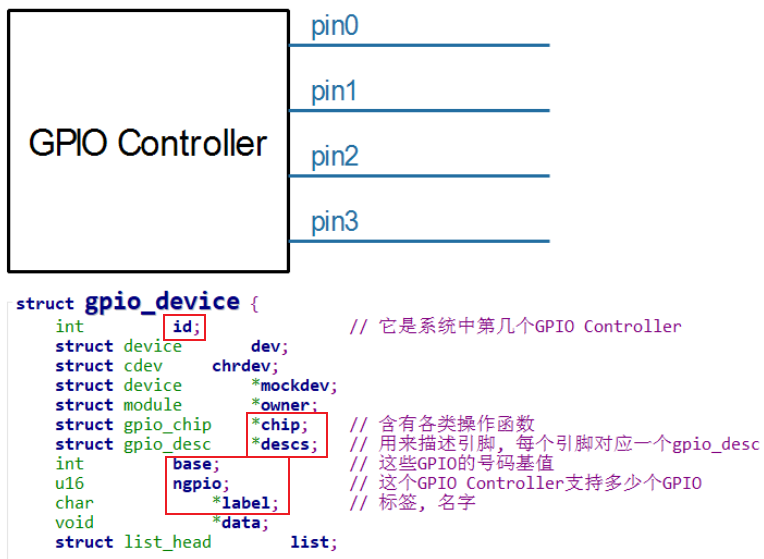
2.1 gpio子系统数据结构 2.1.1 gpio_device 每个GPIO Controller用一个gpio_device来表示:
每组gpio引脚对应一个gpio_desc和一个gpio_chip
gpio引脚的操作函数,都放在gpio_chip成员函数中。
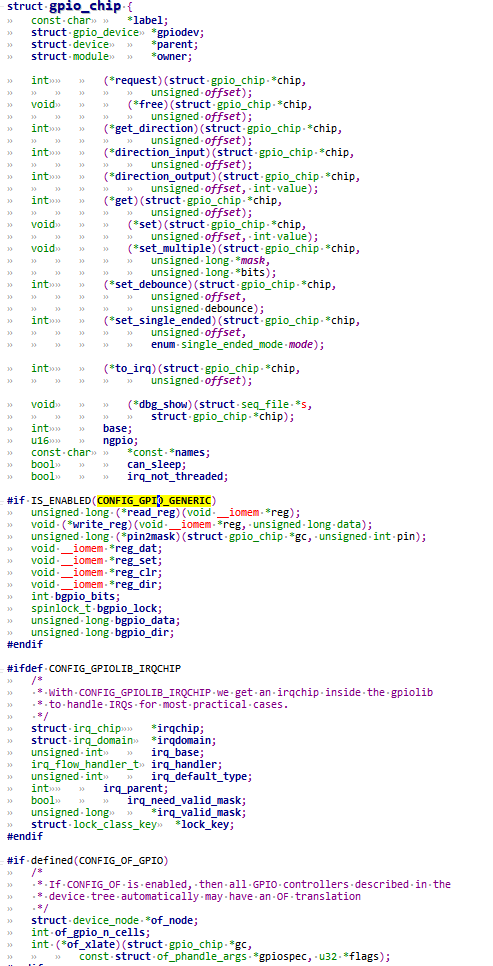
2.1.2 gpio_chip
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 struct gpio_chip { const char *label; struct gpio_device *gpiodev ; struct device *parent ; struct module *owner ; int (*request)(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset); void (*free )(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset); int (*get_direction)(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset); int (*direction_input)(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset); int (*direction_output)(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset, int value); int (*get)(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset); void (*set )(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset, int value); void (*set_multiple)(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned long *mask, unsigned long *bits); int (*set_debounce)(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset, unsigned debounce); int (*set_single_ended)(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset, enum single_ended_mode mode); int (*to_irq)(struct gpio_chip *chip, unsigned offset); void (*dbg_show)(struct seq_file *s, struct gpio_chip *chip); int base; u16 ngpio; const char *const *names; bool can_sleep; bool irq_not_threaded; #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GPIO_GENERIC) unsigned long (*read_reg) (void __iomem *reg) ; void (*write_reg)(void __iomem *reg, unsigned long data); unsigned long (*pin2mask) (struct gpio_chip *gc, unsigned int pin) ; void __iomem *reg_dat; void __iomem *reg_set; void __iomem *reg_clr; void __iomem *reg_dir; int bgpio_bits; spinlock_t bgpio_lock; unsigned long bgpio_data; unsigned long bgpio_dir; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_GPIOLIB_IRQCHIP struct irq_chip *irqchip ; struct irq_domain *irqdomain ; unsigned int irq_base; irq_flow_handler_t irq_handler; unsigned int irq_default_type; int irq_parent; bool irq_need_valid_mask; unsigned long *irq_valid_mask; struct lock_class_key *lock_key ; #endif #if defined(CONFIG_OF_GPIO) struct device_node *of_node ; int of_gpio_n_cells; int (*of_xlate)(struct gpio_chip *gc, const struct of_phandle_args *gpiospec, u32 *flags); #endif
2.1.3 gpio_desc 在gpio_device中有一个gpio_desc数组,每一引脚有一项gpio_desc。
3 gpio子系统api 3.1使用整数的GPIO传统方式 3.1.1 请求和配置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 static int gpio_request (unsigned gpio, const char * label) ;void gpio_free (unsigned gpio) ;static bool gpio_is_valid (unsigned gpio) ;static int gpio_direction_input (unsigned gpio) ;static int gpio_direction_output (unsigned gpio, int value) ; static int gpio_set_debounce (unsigned gpio, unsigned debounce) ;
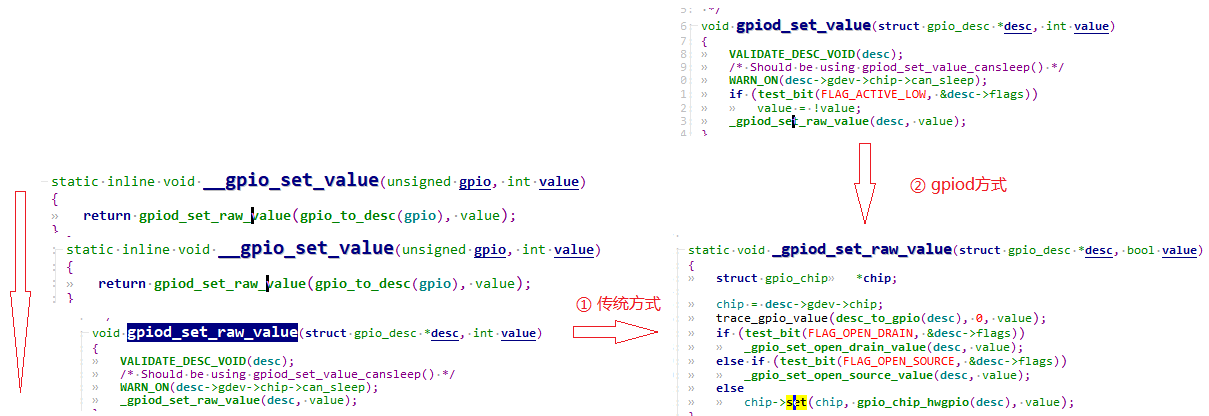
3.1.2 读取和设置值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 static int gpio_get_value (unsigned gpio) ;void gpio_set_value (unsigned gpio, int value) ; bool gpio_cansleep (unsigned gpio) ;static int gpio_get_value_cansleep (unsigned gpio) ;void gpio_set_value_cansleep (unsigned gpio, int value) ; int gpio_to_irq (unsigned gpio) ;int irq_to_gpio (int irq)
3.1.3 gpiochip操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 static inline int gpiochip_add (struct gpio_chip *chip) void gpiochip_remove (struct gpio_chip *chip) gpiochip_line_config gpiochip_request_own gpiochip_request_unown gpiochip_set gpiochip_clear gpiochip_set_direction gpiochip_get_direction
3.2 基于描述符的GPIO方式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 foo_device { compatible = "acme,foo" ; [...]; led-gpios = <&gpio 15 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH> <&gpio 16 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH> <&gpio 17 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH> ; power-gpios = <&gpio 1 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>; reset-gpios = <&gpio 1 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>; };
在代码中获取GPIO的方式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 sruct gpio_desc * gpiod_get_index (struct device *dev, char *con_id, enum gpiod_flags flags) ;sruct gpio_desc * gpiod_get (struct device *dev, char *con_id, enum gpiod_flags flags) ;void gpiod_put (sruct gpio_desc *desc) ;struct gpio_desc *red , *green , *blue , *power , *reset ;red = gpiod_get_index(dev, "led" , 0 , GPIO_OUT_HIGH); green = gpiod_get_index(dev, "led" , 1 , GPIO_OUT_HIGH); blue = gpiod_get_index(dev, "led" , 2 , GPIO_OUT_HIGH); power = gpiod_get(dev, "power" , GPIO_OUT_HIGH); reset = gpiod_get(dev, "reset" , GPIO_OUT_HIGH);
其他类似的功能函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 int gpiod_direction_input (struct gpio_desc *desc) ;int gpiod_direction_output (struct gpio_desc *desc, int value) ;int gpiod_set_debounce (struct gpio_desc *desc, unsigned debounce) ;void gpiod_set_value (struct gpio_desc *desc, int val) ;void gpiod_set_value_cansleep (struct gpio_desc *desc, int val) ;int gpiod_get_value (struct gpio_desc *desc) ;int gpiod_get_value_cansleep (struct gpio_desc *desc) ;struct gpio_desc *gpio_to_desc (unsigned gpio) ;int desc_to_gpio (struct gpio_desc *desc) ;
无论是传统GPIO控制还是基于描述符的gpio方式,都是调用底层控制器gpio_chip的操作函数。
3.3 和设备树相关GPIO接口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 gpio1: gpio1 { gpio-controller; #gpio-cells = <2> ; }; gpio2 : gpio2 { gpio-controller; #gpio-cells = <1> ; }; foo-device { cs-gpios = <&gpio1 17 0 > <&gpio1 2 > <&gpio1 17 0 >; reset-gpio = <&gpio1 30 0 >; cs-gpios = <&gpio2 10 >; }; int n_gpios = of_get_named_gpio_count(dev.of_node, "cs-gpios" );int first_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(dev.of_node, "cs-gpios" );
4 基于sysfs操作gpio 声明GPIO口:
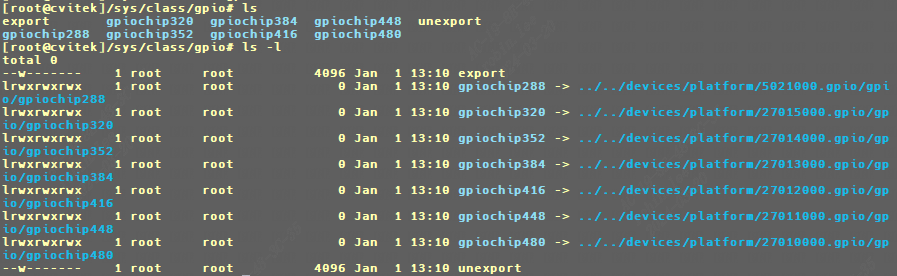
1 2 echo 256 > /sys/class/gpio/export echo 256 > /sys/class/gpio/unexport
方向:
1 2 3 echo "in" > direction echo "out" > direction cat direction
val:
1 2 3 echo 1 > valueecho 0 > valuecat value
edge: "none", "rising","falling","both"。
1 2 3 4 5 none: rising: falling: both: echo "both" > /sys/class/gpio/gpioN/edge
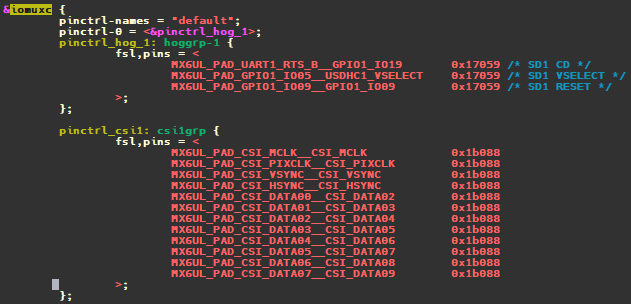
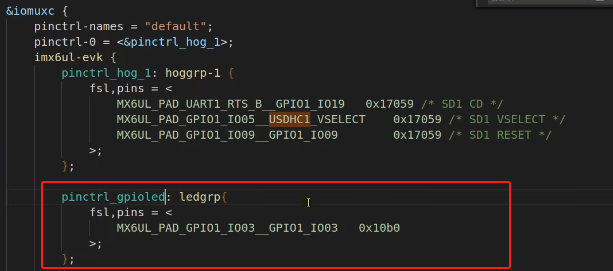
5 gpio子系统示例 以nxp官方evk公板imx6ull-14x14-evk.dts为例:iomuxc引脚控制器,evk设备默认default状态对应的pins为pinctrl_hog_1, 配置3个引脚(UART1_RTS_B, GPIO1_IO05, GPIO1_IO09)信息。看起来是要做成sd卡的热插拔功能。usdhc1和usdhc2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 &usdhc1 { pinctrl-names = "default" , "state_100mhz" , "state_200mhz" ; pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_usdhc1>; pinctrl-1 = <&pinctrl_usdhc1_100mhz>; pinctrl-2 = <&pinctrl_usdhc1_200mhz>; cd-gpios = <&gpio1 19 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>; keep-power-in-suspend; enable-sdio-wakeup; vmmc-supply = <®_sd1_vmmc>; status = "okay" ; };
iomuxc控制器节点下有usdhc1要用的pins信息,包括pinctrl_hog_1,pinctrl_usdhc1,pinctrl_usdhc1_100mhz节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 &iomuxc { pinctrl_usdhc1: usdhc1grp { fsl,pins = < MX6UL_PAD_SD1_CMD__USDHC1_CMD 0x17059 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_CLK__USDHC1_CLK 0x10071 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA0__USDHC1_DATA0 0x17059 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA1__USDHC1_DATA1 0x17059 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA2__USDHC1_DATA2 0x17059 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA3__USDHC1_DATA3 0x17059 >; }; pinctrl_usdhc1_100mhz: usdhc1grp100mhz { fsl,pins = < MX6UL_PAD_SD1_CMD__USDHC1_CMD 0x170b9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_CLK__USDHC1_CLK 0x100b9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA0__USDHC1_DATA0 0x170b9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA1__USDHC1_DATA1 0x170b9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA2__USDHC1_DATA2 0x170b9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA3__USDHC1_DATA3 0x170b9 >; }; pinctrl_usdhc1_200mhz: usdhc1grp200mhz { fsl,pins = < MX6UL_PAD_SD1_CMD__USDHC1_CMD 0x170f9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_CLK__USDHC1_CLK 0x100f9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA0__USDHC1_DATA0 0x170f9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA1__USDHC1_DATA1 0x170f9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA2__USDHC1_DATA2 0x170f9 MX6UL_PAD_SD1_DATA3__USDHC1_DATA3 0x170f9 >; }; }
5.1 gpio控制器dts描述 前面讲的其实都还是pinctrl的内容,usdhc1有一个属性cd-gpios。这时就需要用到gpio控制器了,以imx6ull为例,gpio控制器描述如下:
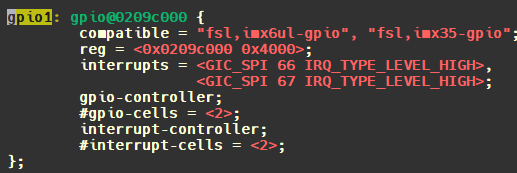
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Linux-4.9 .88 /Documentation/devicetree/bindings/gpio$ ls -l fsl-imx-gpio.txt * Freescale i.MX/MXC GPIO controller Required properties: - compatible : Should be "fsl,<soc>-gpio" - reg : Address and length of the register set for the device - interrupts : Should be the port interrupt shared by all 32 pins, if one number. If two numbers, the first one is the interrupt shared by low 16 pins and the second one is for high 16 pins. - gpio-controller : Marks the device node as a gpio controller. - #gpio-cells : Should be two. The first cell is the pin number and the second cell is used to specify the gpio polarity: 0 = active high 1 = active low - interrupt-controller: Marks the device node as an interrupt controller. - #interrupt-cells : Should be 2. The first cell is the GPIO number. The second cell bits[3 :0 ] is used to specify trigger type and level flags: 1 = low-to-high edge triggered. 2 = high-to-low edge triggered. 4 = active high level-sensitive. 8 = active low level-sensitive. Example: gpio0: gpio@73f 84000 { compatible = "fsl,imx51-gpio" , "fsl,imx35-gpio" ; reg = <0x73f84000 0x4000 >; interrupts = <50 51 >; gpio-controller; #gpio-cells = <2> ; interrupt-controller; #interrupt-cells = <2> ; };
打开具体的imx6ull.dtsi:
5.2 gpio控制器使用者 回到usdhc1的属性cd-gpios。
1 cd-gpios = <&gpio1 19 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
表述使用gpio1控制器,由于该控制器的gpio-cells为2, 根据描述:
1 2 3 4 the second cell is used to specify the gpio polarity: 0 = active high 1 = active low
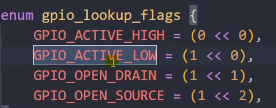
19表示pin number, GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW是一个宏定义:可以看到为1,也就是低电平有效
5.2.1 使用者操作流程 1 2 3 4 5 1. of_find_node_by_path获取使用该gpio的节点2. of_get_named_gpio,获取gpio编号3. gpio_request,申请gpio4. gpio_direction_set/gpio_direction_get5. gpio_val_set
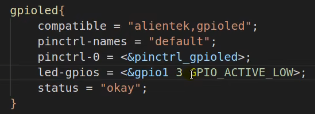
5.2.1.1 dts自定义gpio控制器使用者(demo1,gpio_led) 编写一个gpioled节点:
iomuxc节点,因为用到了GPIO1_IO03,要设置该pin脚为gpio:
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 #include <linux/types.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/delay.h> #include <linux/ide.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/errno.h> #include <linux/gpio.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/of.h> #include <linux/of_address.h> #include <linux/of_gpio.h> #include <asm/mach/map.h> #include <asm/uaccess.h> #include <asm/io.h> #define GPIOLED_CNT 1 #define GPIOLED_NAME "gpioled" #define LEDOFF 0 #define LEDON 1 struct gpioled_dev { dev_t devid; struct cdev cdev ; struct class *class ; struct device *device ; int major; int minor; struct device_node *nd ; int led_gpio; }; struct gpioled_dev gpioled ;static int led_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { filp->private_data = &gpioled; return 0 ; } static ssize_t led_read (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt) { return 0 ; } static ssize_t led_write (struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt) { int retvalue; unsigned char databuf[1 ]; unsigned char ledstat; struct gpioled_dev *dev = retvalue = copy_from_user(databuf, buf, cnt); if (retvalue < 0 ) { printk("kernel write failed!\r\n" ); return -EFAULT; } ledstat = databuf[0 ]; if (ledstat == LEDON) { gpio_set_value(dev->led_gpio, 0 ); } else if (ledstat == LEDOFF) { gpio_set_value(dev->led_gpio, 1 ); } return 0 ; } static int led_release (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { return 0 ; } static struct file_operations gpioled_fops = .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = led_open, .read = led_read, .write = led_write, .release = led_release, }; static int __init led_init (void ) { int ret = 0 ; gpioled.nd = of_find_node_by_path("/gpioled" ); if (gpioled.nd == NULL ) { printk("gpioled node not find!\r\n" ); return -EINVAL; } else { printk("gpioled node find!\r\n" ); } gpioled.led_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(gpioled.nd, "led-gpio" , 0 ); if (gpioled.led_gpio < 0 ) { printk("can't get led-gpio" ); return -EINVAL; } printk("led-gpio num = %d\r\n" , gpioled.led_gpio); ret = gpio_direction_output(gpioled.led_gpio, 1 ); if (ret < 0 ) { printk("can't set gpio!\r\n" ); } if (gpioled.major) { gpioled.devid = MKDEV(gpioled.major, 0 ); register_chrdev_region(gpioled.devid, GPIOLED_CNT, GPIOLED_NAME); } else { alloc_chrdev_region(&gpioled.devid, 0 , GPIOLED_CNT, GPIOLED_NAME); gpioled.major = MAJOR(gpioled.devid); gpioled.minor = MINOR(gpioled.devid); } printk("gpioled major=%d,minor=%d\r\n" ,gpioled.major, gpioled.minor); gpioled.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE; cdev_init(&gpioled.cdev, &gpioled_fops); cdev_add(&gpioled.cdev, gpioled.devid, GPIOLED_CNT); gpioled.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, GPIOLED_NAME); if (IS_ERR(gpioled.class)) { return PTR_ERR(gpioled.class); } gpioled.device = device_create(gpioled.class, NULL , gpioled.devid, NULL , GPIOLED_NAME); if (IS_ERR(gpioled.device)) { return PTR_ERR(gpioled.device); } return 0 ; } static void __exit led_exit (void ) { cdev_del(&gpioled.cdev); unregister_chrdev_region(gpioled.devid, GPIOLED_CNT); device_destroy(gpioled.class, gpioled.devid); class_destroy(gpioled.class); } module_init(led_init); module_exit(led_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL" );
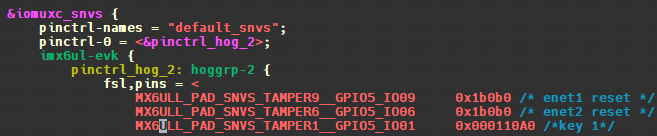
5.2.1.2 dts自定义gpio控制器使用者(demo2,beep) evk公板的蜂鸣器。BEEP使用了SNVS_TAMPER1这个PIN,打开imx6ull-alientek-emmc.dts,SNVS_TAMPER1属于iomuxc_snvs这个pin controller。iomuxc节点的imx6ul-evk子节点下创建一个名为“pinctrl_beep”的子节点:
1 2 3 4 5 pinctrl_beep: beepgrp { fsl,pins = < MX6ULL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER1__GPIO5_IO01 0x10B0 >; };
根节点“/”下创建BEEP节点:可以看到用到了引脚控制器的pinctrl_beep节点。同时使用gpio子系统,beep-gpio属性用到gpio5控制器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 beep { #address-cells = <1> ; #size-cells = <1> ; compatible = "evk-beep" ; pinctrl-names = "default" ; pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_beep>; beep-gpio = <&gpio5 1 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; status = "okay" ; };
蜂鸣器使用的 PIN 为 SNVS_TAMPER1,因此先检查 PIN 为SNVS_TAMPER1 这个 PIN 有没有被其他的 pinctrl 节点使用,如果有使用的话就要屏蔽掉,然后再检查 GPIO5_IO01 这个 GPIO 有没有被其他外设使用,如果有的话也要屏蔽掉。
输入“make dtbs”命令重新编译设备树,然后使用新编译出来的 imx6ull-alientek-emmc.dtb 文件启动 Linux 系统,进入“/proc/device-tree”目录中 查看“beep”节点是否存在:
点击查看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 #include <linux/types.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/delay.h> #include <linux/ide.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/errno.h> #include <linux/gpio.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/of.h> #include <linux/of_address.h> #include <linux/of_gpio.h> #include <asm/mach/map.h> #include <asm/uaccess.h> #include <asm/io.h> #define BEEP_CNT 1 #define BEEP_NAME "beep" #define BEEPOFF 0 #define BEEPON 1 struct beep_dev { dev_t devid; struct cdev cdev ; struct class *class ; struct device *device ; int major; int minor; struct device_node *nd ; int beep_gpio; }; struct beep_dev beep ;static int beep_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { filp->private_data = &beep; return 0 ; } static ssize_t beep_write (struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt) { int retvalue; unsigned char databuf[1 ]; unsigned char beepstat; struct beep_dev *dev = retvalue = copy_from_user(databuf, buf, cnt); if (retvalue < 0 ) { printk("kernel write failed!\r\n" ); return -EFAULT; } beepstat = databuf[0 ]; if (beepstat == BEEPON) { gpio_set_value(dev->beep_gpio, 0 ); } else if (beepstat == BEEPOFF) { gpio_set_value(dev->beep_gpio, 1 ); } return 0 ; } static int beep_release (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { return 0 ; } static struct file_operations beep_fops = .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = beep_open, .write = beep_write, .release = beep_release, }; static int __init beep_init (void ) { int ret = 0 ; beep.nd = of_find_node_by_path("/beep" ); if (beep.nd == NULL ) { printk("beep node not find!\r\n" ); return -EINVAL; } else { printk("beep node find!\r\n" ); } beep.beep_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(beep.nd, "beep-gpio" , 0 ); if (beep.beep_gpio < 0 ) { printk("can't get beep-gpio" ); return -EINVAL; } printk("led-gpio num = %d\r\n" , beep.beep_gpio); ret = gpio_direction_output(beep.beep_gpio, 1 ); if (ret < 0 ) { printk("can't set gpio!\r\n" ); } if (beep.major) { beep.devid = MKDEV(beep.major, 0 ); register_chrdev_region(beep.devid, BEEP_CNT, BEEP_NAME); } else { alloc_chrdev_region(&beep.devid, 0 , BEEP_CNT, BEEP_NAME); beep.major = MAJOR(beep.devid); beep.minor = MINOR(beep.devid); } printk("beep major=%d,minor=%d\r\n" ,beep.major, beep.minor); beep.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE; cdev_init(&beep.cdev, &beep_fops); cdev_add(&beep.cdev, beep.devid, BEEP_CNT); beep.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, BEEP_NAME); if (IS_ERR(beep.class)) { return PTR_ERR(beep.class); } beep.device = device_create(beep.class, NULL , beep.devid, NULL , BEEP_NAME); if (IS_ERR(beep.device)) { return PTR_ERR(beep.device); } return 0 ; } static void __exit beep_exit (void ) { cdev_del(&beep.cdev); unregister_chrdev_region(beep.devid, BEEP_CNT); device_destroy(beep.class, beep.devid); class_destroy(beep.class); } module_init(beep_init); module_exit(beep_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL" );
核心代码分析:
1 2 3 4 1. of_find_node_by_path("/beep" );2. of_get_named_gpio(beep.nd, "beep-gpio" , 0 );3. gpio_direction_output(beep.beep_gpio, 1 );4. gpio_set_value(dev->beep_gpio, 0 );
注意这里并没有使用pinctrl, pinctrl子系统是内核启动时就对pinctrl(也叫iomuxc)控制器进行了配置,进行了IOMUX配置。因此SNVS_TAMPER1会复用成gpio模式。
按键作为输入时:
static int keyio_init(void)
{
keydev.nd = of_find_node_by_path("/key");
if (keydev.nd== NULL) {
return -EINVAL;
}
keydev.key_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(keydev.nd ,"key-gpio", 0);
if (keydev.key_gpio < 0) {
printk("can't get key0\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
printk("key_gpio=%d\r\n", keydev.key_gpio);
/* 初始化key所使用的IO */
gpio_request(keydev.key_gpio, "key0"); /* 请求IO */
gpio_direction_input(keydev.key_gpio); /* 设置为输入 */
return 0;
}